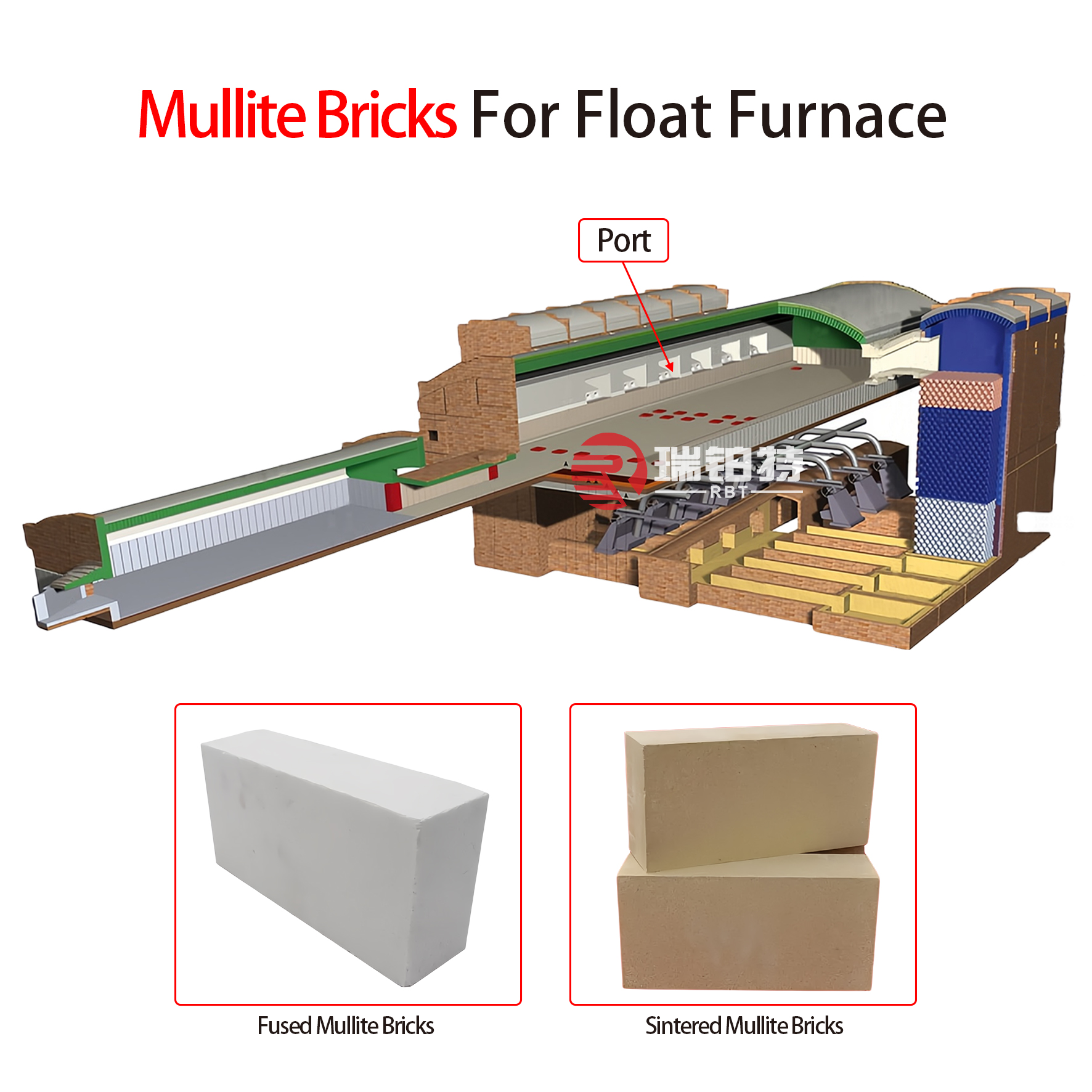
Taking float glass as an example, the three major thermal equipment in glass production include float glass melting furnace, float glass tin bath and glass annealing furnace. In the process of glass production, the glass melting furnace is responsible for melting the batch materials into glass liquid and clarifying, homogenizing and cooling them to the temperature required for molding. The tin bath is the key equipment for glass molding. The glass liquid with a temperature of 1050~1100℃ flows from the flow channel to the tin liquid surface in the tin bath. The glass liquid is flattened and polished on the surface of the tin bath, and is controlled by mechanical pulling, side guards and side drawing machines to form a glass ribbon of the required width and thickness. And it leaves the tin bath when it gradually cools to 600℃ during the forward process. The function of the annealing furnace is to eliminate the residual stress and optical inhomogeneity of float glass, and to stabilize the internal structure of the glass. The continuous glass ribbon with a temperature of about 600℃ caused by the tin bath enters the annealing furnace through the transition roller table. All of these three major thermal equipment require refractory materials. To ensure the normal and stable operation of the glass melting furnace, it is indeed inseparable from the support of a variety of refractory materials. The following are 9 types of refractory materials commonly used in glass melting furnaces and their characteristics:

Silica bricks for glass kilns:
Main ingredients: silicon dioxide (SiO2), the content is required to be above 94%. Operating temperature: the highest operating temperature is 1600~1650℃. Features: good resistance to acidic slag erosion, but poor resistance to alkaline flying material erosion. Mainly used for masonry of large arches, breast walls and small furnaces.
Fire Clay bricks for glass kilns:
Main ingredients: Al2O3 and SiO2, Al2O3 content is between 30%~45%, SiO2 is between 51%~66%. Operating temperature: the highest operating temperature is 1350~1500℃. Features: It is a weakly acidic refractory material with good refractoriness, thermal stability and low thermal conductivity. Mainly used for masonry of the bottom of the kiln pool, the pool wall of the working part and the passage, the wall, arch, lower checker bricks and flue of the heat storage room.
High alumina bricks for glass kilns:
Main components: SiO2 and Al2O3, but the Al2O3 content should be greater than 46%. Operating temperature: The maximum operating temperature is 1500~1650℃. Features: Good corrosion resistance, and can resist corrosion from both acidic and alkaline slags. Mainly used in heat storage chambers, as well as refractory accessories for working pools, material channels and feeders.
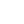
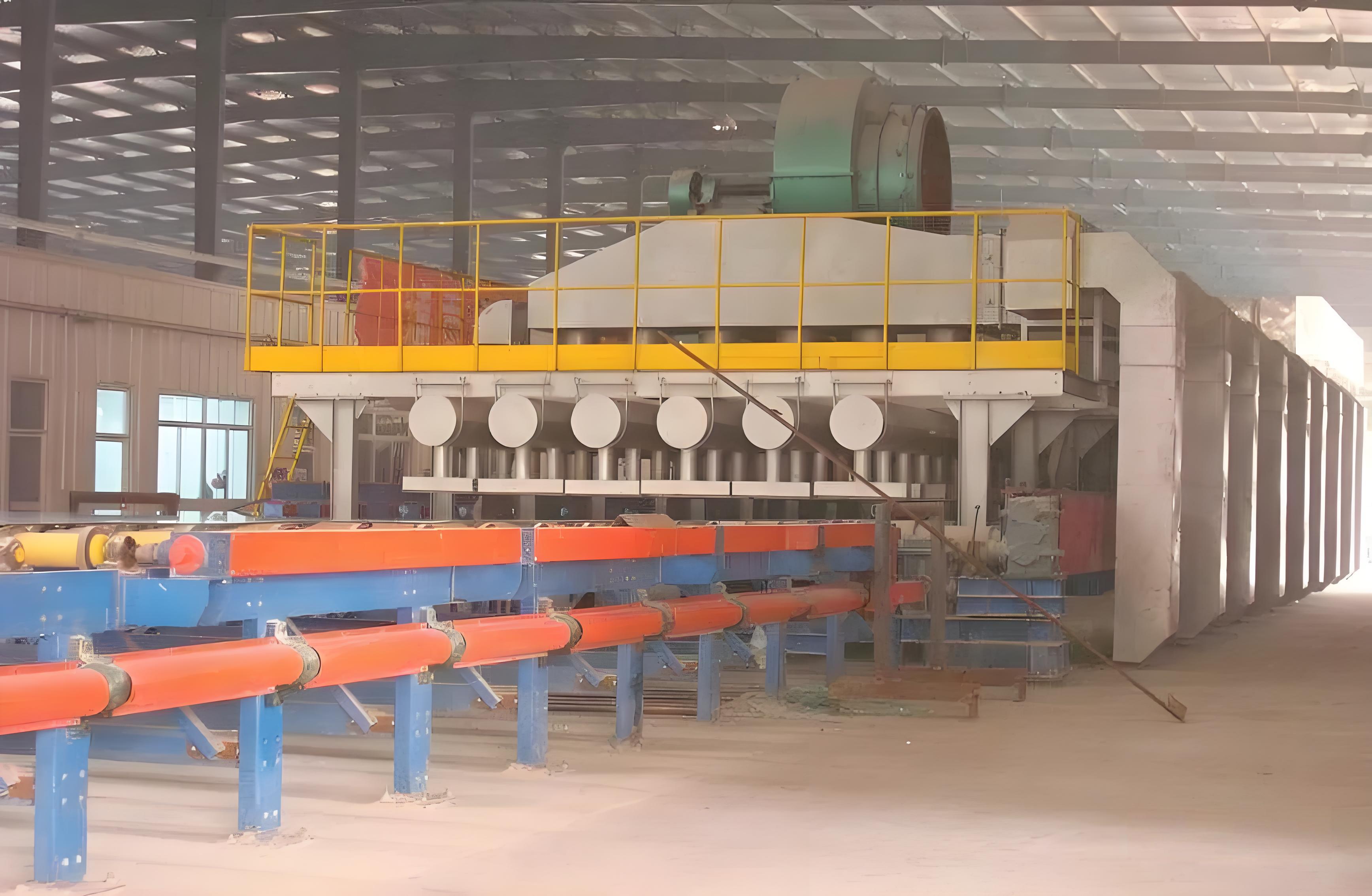
Mullite bricks:
The main component of mullite bricks is Al2O3, and its content is about 75%. Because it is mainly mullite crystals, it is called mullite bricks. Density 2.7-3 2g/cm3, open porosity 1%-12%, and the maximum operating temperature is 1500~1700℃. Sintered mullite is mainly used for masonry of heat storage chamber walls. Fused mullite is mainly used for masonry of pool walls, observation holes, wall buttresses, etc.
Fused zirconium corundum bricks:
Fused zirconium corundum bricks are also called white iron bricks. Generally, fused zirconium corundum bricks are divided into three grades according to the zirconium content: 33%, 36%, and 41%. The zirconium corundum bricks used in the glass industry contain 50%~70% Al2O3 and 20%~40% ZrO2. The density is 3.4~4.0g/cm3, the apparent porosity is 1%~10%, and the maximum operating temperature is about 1700℃. Fused zirconium corundum bricks with a zirconium content of 33% and 36% are used to build kiln pool walls, flame space breast walls, small furnace blast holes, small furnace flat arches, small furnace stacks, tongue arches, etc. Fused zirconium corundum bricks with a zirconium content of 41% are used to build pool wall corners, flow holes, and other parts where the glass liquid erodes and corrodes the refractory materials most violently. This material is the most widely used fused cast refractory material in the glass industry.
Fused alumina bricks:
It mainly refers to fused α, β corundum, and fused β corundum refractory bricks, which are mainly composed of 92%~94% Al2O3 corundum crystal phase, density 2.9~3.05g/cm3, apparent porosity 1%~10%, and maximum operating temperature of about 1700℃. Fused alumina has excellent resistance to glass permeation and almost no pollution to glass liquid. It is widely used in the working part pool wall, pool bottom, flow channel, working part material channel pool wall, material channel pool bottom and other parts of the glass melting furnace that contact the glass liquid and require no refractory contamination.
Quartz bricks:
The main component is SiO2, which contains more than 99%, with a density of 1.9~2g/cm3, a refractoriness of 1650℃, a working temperature of about 1600℃, and acid erosion resistance. It is used to build the pool wall of acidic boron glass, flame space thermocouple hole bricks, etc.
Alkaline refractory materials:
Alkaline refractory materials mainly refer to magnesia bricks, alumina-magnesia bricks, magnesia-chrome bricks, and forsterite bricks. Its performance is to resist the erosion of alkaline materials, and its refractoriness is 1900~2000℃. It is widely used in the upper wall of the regenerator of the glass melting furnace, the regenerator arch, the grid body, and the small furnace part structure.
Insulation bricks for glass furnaces:
The heat dissipation area of the glass melting furnace is large and the thermal efficiency is low. In order to save energy and reduce consumption, a large amount of insulation materials are needed for comprehensive insulation. In particular, the pool wall, pool bottom, arch, and wall in the regenerator, melting part, working part, etc. should be insulated to reduce heat dissipation. The porosity of the insulation brick is very large, the weight is very light, and the density does not exceed 1.3g/cm3. Since the heat transfer performance of air is very poor, the insulation brick with a large porosity has an insulating effect. Its thermal conductivity coefficient is 2~3 times lower than that of general refractory materials, so the larger the porosity, the better the insulation effect. There are many different types of insulation bricks, including clay insulation bricks, silica insulation bricks, high alumina insulation bricks and so on.






Post time: Apr-25-2025