Cement Kiln Castable Construction Process Display
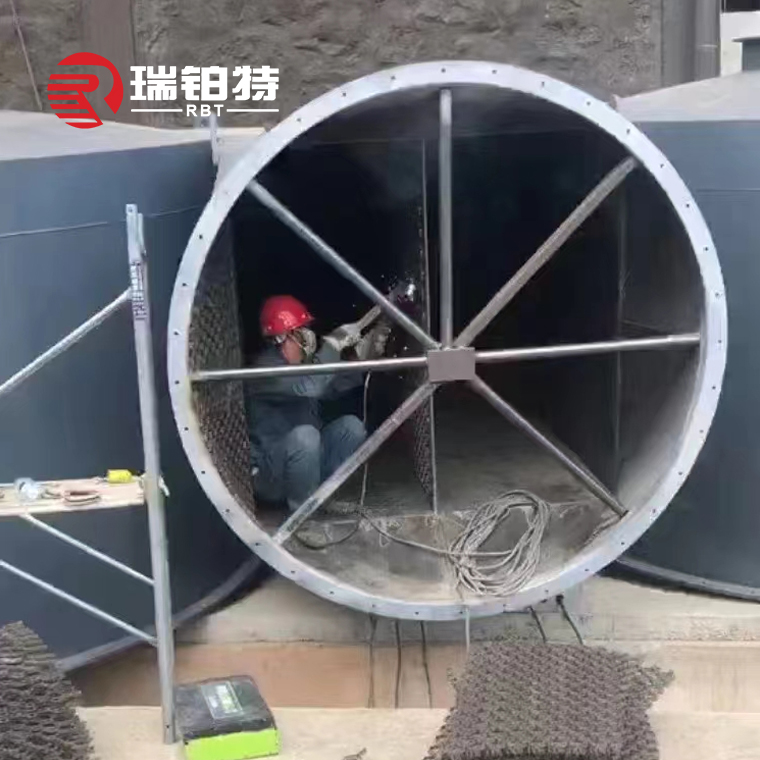
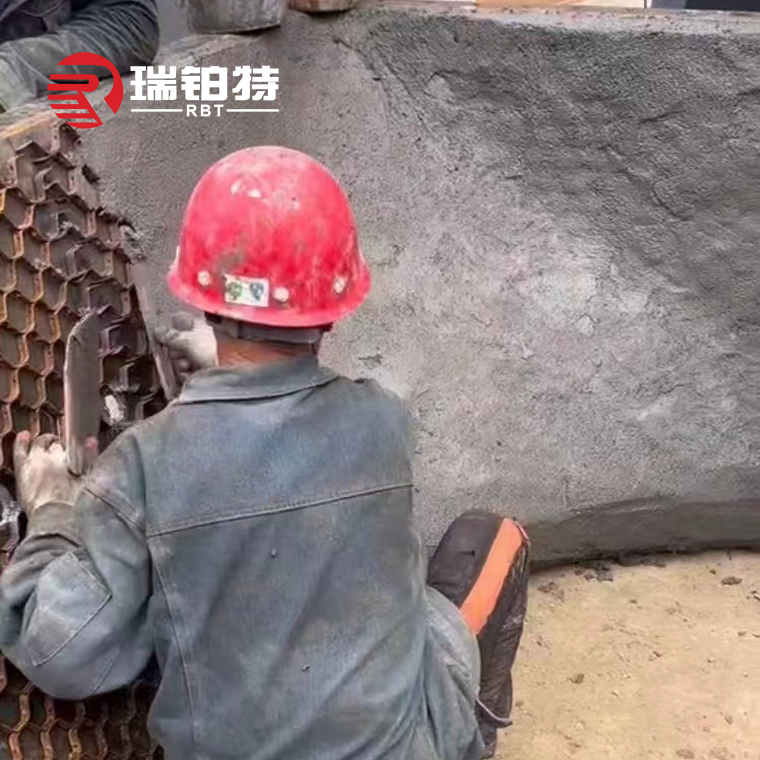
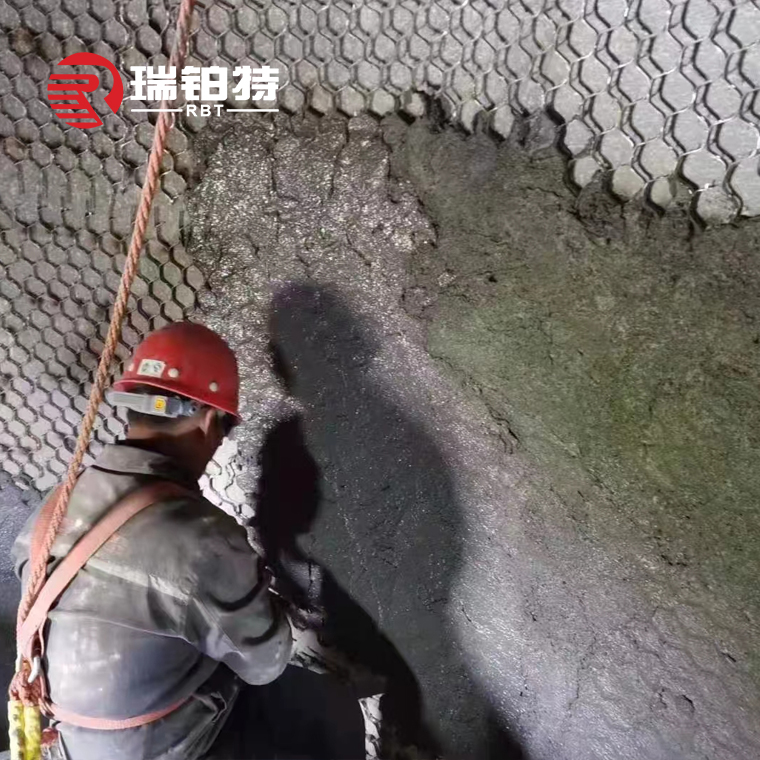




Refractory Castables For Cement Rotary Kiln
1. Steel fiber reinforced refractory castables for cement kiln
Steel fiber reinforced castables mainly introduce heat-resistant stainless steel fibers into the material, so that the material has higher strength and thermal shock resistance, thereby increasing the wear resistance and service life of the material. The material is mainly used for high-temperature wear-resistant parts such as kiln mouth, feeding mouth, wear-resistant pier and power plant boiler lining.
2. Low cement refractory castables for cement kiln
Low cement refractory castables mainly include high-alumina, mullite and corundum refractory castables. This series of products has the characteristics of high strength, anti-scouring, wear resistance and excellent performance. At the same time, the material can be made into fast-baking explosion-proof castables according to the user's baking time requirements.
3. High-strength alkali-resistant castables for cement kiln
High-strength alkali-resistant castables have good resistance to erosion by alkaline gases and slag, and have a long service life. This material is mainly used for kiln door covers, decomposition furnaces, preheater systems, management systems, etc. and other industrial kiln linings.
Construction method of high-aluminum low-cement castable for rotary kiln lining
The construction of high-aluminum low-cement castable for rotary kiln lining requires special attention to the following five processes:
1. Determination of expansion joints
Based on the previous experience of using high-aluminum low-cement castables, expansion joints are a key factor affecting the service life of rotary kiln castable linings. The expansion joints during the pouring of rotary kiln linings are determined as follows:
(1) Circumferential joints: 5m sections, 20mm aluminum silicate fiber felt is sandwiched between the castables, and the fibers are compacted after expansion to buffer the expansion stress.
(2) Flat joints: Every three strips of the castable are sandwiched with 100mm deep plywood in the inner circumferential direction, and a joint is left at the working end, for a total of 6 strips.
(3) During pouring, 25 exhaust pins are used per square meter to release a certain amount of expansion stress while exhausting the kiln.
2. Determination of construction temperature
The suitable construction temperature of high-aluminum low-cement castables is 10~30℃. If the ambient temperature is low, the following measures should be taken:
(1) Close the surrounding construction environment, add heating facilities, and strictly prevent freezing.
(2) Use hot water at 35-50℃ (determined by the on-site pouring test vibration) to mix the material.
3. Mixing
Determine the mixing amount at one time according to the capacity of the mixer. After the mixing amount is determined, add the casting material in the bag and the small package additives in the bag into the mixer at the same time. First start the mixer to dry-mix for 2~3 minutes, then add 4/5 of the weighed water first, stir for 2~3 minutes, and then determine the remaining 1/5 of the water according to the viscosity of the mud. After fully mixing, test pouring is carried out, and the amount of water added is determined in combination with the vibration and slurry situation. After the amount of water added is determined, it must be strictly controlled. While ensuring that the slurry can be vibrated, as little water as possible should be added (the reference water addition amount for this castable is 5.5%-6.2%).
4. Construction
The construction time of high-aluminum low-cement castable is about 30 minutes. The dehydrated or condensed materials cannot be mixed with water and should be discarded. Use a vibrating rod to vibrate to achieve slurry compaction. The vibrating rod should be spared to prevent the spare rod from being activated when the vibrating rod fails.
The construction of the castable material should be carried out in strips along the axis of the rotary kiln. Before each strip pouring, the construction surface should be cleaned and no dust, welding slag and other debris should be left. At the same time, check whether the welding of the anchor and the surface asphalt paint treatment are in place. Otherwise, remedial measures should be taken.
In the strip construction, the construction of the strip casting body should be openly poured from the kiln tail to the kiln head at the bottom of the kiln body. The support of the template should be carried out between the anchor and the steel plate. The steel plate and the anchor are firmly inlaid with wooden blocks. The support formwork height is 220mm, width is 620mm, length is 4-5m, and the center angle is 22.5°.
The construction of the second casting body should be carried out after the strip is finally set and the mold is removed. On one side, the arc-shaped template is used to close the casting from the kiln head to the kiln tail. The rest is analogous.
When the casting material is vibrated, the mixed mud should be added into the tire mold while vibrating. The vibration time should be controlled so that there are no obvious bubbles on the surface of the casting body. The demoulding time should be determined by the ambient temperature of the construction site. It is necessary to ensure that the demoulding is carried out after the casting material is finally set and has a certain strength.
5. Baking of lining
The baking quality of the rotary kiln lining directly affects the service life of the lining. In the previous baking process, due to the lack of mature experience and good methods, the method of injecting heavy oil for combustion was used in the low-temperature, medium-temperature and high-temperature baking processes. The temperature was difficult to control: when the temperature needs to be controlled below 150℃, the heavy oil is not easy to burn; when the temperature is higher than 150℃, the heating speed is too fast, and the temperature distribution in the kiln is very uneven. The temperature of the lining where the heavy oil is burned is about 350~500℃ higher, while the temperature of other parts is low. In this way, the lining is easy to burst (the previous castable lining has burst during the baking process), affecting the service life of the lining.
Post time: Jul-10-2024